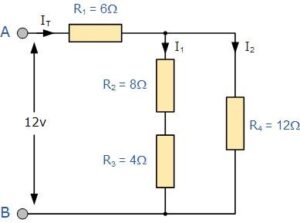
A complex resistance circuit is made up of a large number of resistors connected in series and in parallel.
It will form a complex resistance network. We need to think about calculating the sum of the circuit resistance, current, and voltage of these resistance combinations.
A resistor combination or hybrid resistor circuit is a resistor circuit that combines series and parallel resistor networks. The calculation method of the circuit in series or parallel is the same as the method of equivalent resistance. The resistors connected in series carry exactly the same current, and the resistors connected in parallel have exactly the same voltage.
Step 1
The method of calculating the total current (IT) obtained by the 12v power supply in the circuit is as follows:
Step 2
Through careful observation, we can see two resistors. R 2 and R 3 are combined. The addition of R 2 and R 3 produces the same resistance. The combined resistance of this combination is R 2 + R 3 =8Ω+4Ω=12Ω. We can replace R 2 and R 3 with 12Ω.
Step 3
There is a resistor R A and a resistor R 4 in the “PARALLEL” of the circuit. For the resistors in the parallel equation, we can use the following two parallel resistor formulas to reduce the parallel combination to a single equivalent resistance value R (combination).
The resistance circuit is as follows:
Step 4
Next, R 1 and R (combing) are naturally connected together. Their resistance can also be added. The resistance is as follow:
R = R comb + R 1 = 6Ω+6Ω = 12Ω
Step 5
We can replace the original four resistors with a 12Ω resistor. We now use Ohm’s law to calculate the current.
Step 6
By using the above steps, we can replace the complex resistance circuit with the resistance connected in series or parallel. A resistor composed of several resistors will be simplified into a single circuit with an equivalent resistance. We can find two branch currents by the Ohm method, I 1 and I 2.
V (R1) = I * R 1 = 1 * 6 = 6 volts
V (RA) = V R4 = (12-V R1) = 6 volts
I 1 = 6V÷R A = 6÷12 = 0.5A or 500mA
I 2 = 6V÷R 4 = 6÷12 = 0.5A or 500mA
The resistance value of the two branches is the same at 12Ω. Both I 1 and I 2 are 0.5A (or 500mA). Total power supply current I T: 0.5 + 0.5 = 1.0 ampere.
Conclusion
For any circuit composed of resistances of series and parallel branches, what we need to do is to identify simple series and parallel resistance branches and replace them with equivalent resistances.
In this way, we can simplify complex circuits. It helps us to convert a complex combined resistance circuit into a single equivalent resistance.
We can use complex resistor combinations and resistor networks to draw or redraw new circuits. This helps visual aids in mathematics. Then we can find an equivalent resistance R EQ by changing the series or parallel combination.
By(easybom)


















Leave a Reply